Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are scam
Let`s find out why people think NFTs is a scam, and how you can protect yourself from these bad NFT artists.
June 1, 2022
In 2021, the NFT marketplace declared a total market value of over $40 billion, with celebrity endorsements from the likes of Snoop Dog, Mark Cuban and many others. Whether they support non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or not, investors from different sectors cannot ignore this new trend. However, despite the rapid growth of NFTs, there are still many criticisms and questions about their legitimacy. This guide will provide you with an in-depth understanding of the value of NFTs, to help you answer those who think NFTs are scams.
Why people think NFTs are scams?

Since their inception, a number of people have viewed NFTs as an old-fashioned scam in a high-tech guise. They see them as overpriced JPEG files, a terrible idea and full of problems.
Here are some reasons:
- NFTs are illiquid and volatile: many people buy NFTs without understanding the implications of illiquidity and invest money they cannot afford to lose,
- Environmental impact, as the most popular NFT marketplaces run on the Ethereum blockchain, which uses an energy-intensive mining protocol called proof of work,
- They are only valuable as tools for money laundering, tax evasion and investment fraud. While the integrity of blockchain technology is unquestioned, NFTs can perpetuate fraud. For example, a number of artists have discovered their work being sold as NFTs on NFT marketplaces without their consent.
At AirNFTs, we believe that instead of calling all NFT projects scams, people should broaden their understanding and elaborate more on the diversity and future use cases offered by NFTs.
NFT are everywhere, beyond digital artworks, and there is tremendous untapped potential in the NFT market. We talked more about the Future of NFTs in a previous article but here are some interesting examples:
- Medical records and identity verification: NFT ledgers can store a person's medical records without compromising confidentiality,
- Intellectual property and patents: NFT tokens allow users to prove their ownership of a piece of content,
- Gaming Industry: the integration of NFT into the gaming industry is a popular use case that will most likely be part of the future of gaming. Play-to-Earn gaming is booming, although it is only a small subset of the huge online gaming market. In-game NFT items combine the aspects of utility and collectibility for players.
Before generalizing all NFTs as scams, it is best to make a clear distinction between the concept itself (what an NFT is) and the malicious actors who create these scams.
How do NFT scams work?
NFT scams work by either stealing your crypto wallet's login credentials or by tricking you into believing that you have successfully bought or sold a legitimate NFT. Many cybercriminals are attracted by the monetary value attached to these digital assets, so they adapt their usual hacking methods, such as phishing, to break into cryptocurrency users' accounts and steal NFTs. We'll discuss this in more detail below.
How to recognize an NFT scam?
They fall into several categories, let's look at some of them:
1. The Rug pull or fake NFT projects
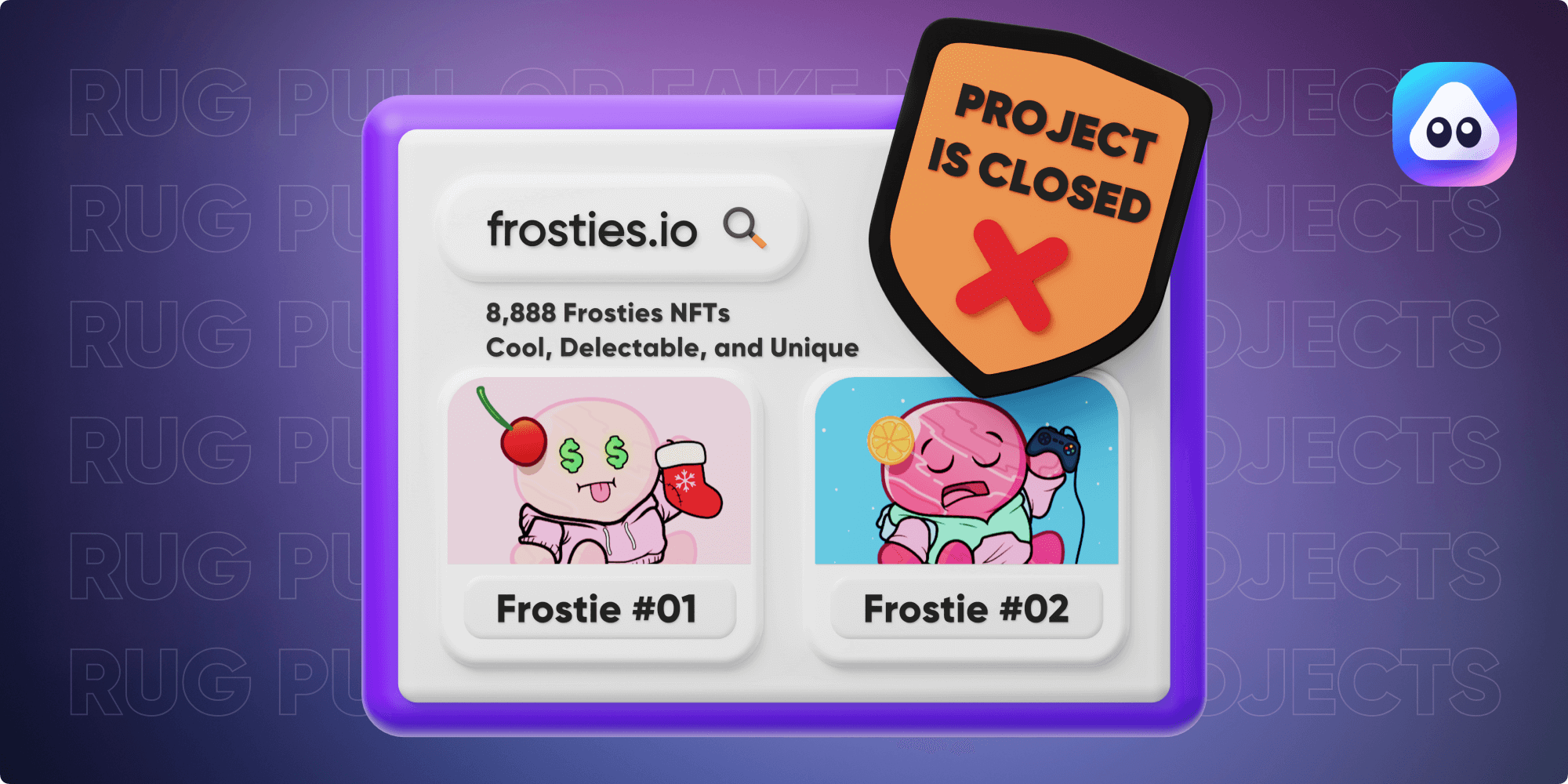
It is literally a scam run by illegitimate NFT creators. In simple terms, a [Rug Pull](http://www.airnfts.com/post/ nfts-and-rug-pulls-how-to-stay-safe) is when a scammer lures you into what appears to be a legitimate NFT project. Right after its launch, the developers suddenly leave and disappear. Unfortunately, they get away with all your funds. Although you still have the token, coin or NFT, at this point it is already worthless.
Only buy NFTs from trustworthy NFT marketplaces, such as AirNFTs, or OpenSea, where the artists are verified and where there are complaint and refund procedures.
2. Plagiarized or fake NFTs and art theft

Scammers simply sell digital images, without actually minting NFTs. These projects are often accompanied by social media campaigns, promises of incredible value and very little knowledge about the NFT creator. As the money comes in, the scammers wait for their exit. Buyers receive something, usually a JPEG attached to an email, and the scammers disappear with their money and email address. Because [NFT verification](http://NFTs and Intellectual Property: What You Should Know) is not simple for uninitiated buyers, this scam can be devastating to a wide audience.
If you are buying an NFT, as always, do your research. Check the seller's account verification. On AirNFTs, this is a blue verification badge. Follow the seller on social media and also check their history on NFT marketplaces. Also look for complaints. If the artwork was stolen, you'll likely find traces of the real owners online.
3. Phishing scams

Phishing scams are nothing new, but in the complex world of NFTs and crypto, it can be easy to fall for them if you are new to the technology. New NFT offerings come out in rapid succession, and it's easy to get caught up in the hype. Scammers will often ask you for your security details or wallet address. Never give out information willingly and never give out your 12-word seed phrase - and keep it offline, ideally on a USB stick.
To stay safe, only share your wallet details with sites you trust, and never give out details if asked. Only give out details when you visit a site yourself, without being linked to it by an email or Twitter post.
How to avoid NFT scams?
Due diligence is required. We discussed this in more detail in our previous article on "How to validate the authenticity of an NFT". Here are some of the things users should consider:
- Never click on suspicious links or attachments,
- Create strong passwords for your wallets and NFT accounts,
- Enable two-factor authentication,
- Verify the NFT creator's account and their socials,
- Never share your seed/recovery phrase.
Should you invest in NFTs?
Not all NFTs are scams, but you should know that most of them have no inherent value or utility behind them. Some do, especially in crypto-games, but most NFTs are mere collectibles that can't earn you passive income if they aren't traded. As an investor, you need to understand the value of the underlying asset that NFT represents before you buy.
Closing thoughts
When you buy and sell NFTs, you don't have many safeguards to protect you from scams, price gouging, etc. People often get scammed by buying or selling illegitimate NFTs from an entity that claims to be a verified NFT project. You should trade NFTs on secure NFT marketplaces such as AirNFTs and always do your own research before throwing money in an NFT project.
